
Furthermore, all patients will be categorized based on the indication for coronary angiography (acute coronary syndrome, chronic coronary syndrome, preoperative coronary angiography) and on the severity of CAD using the SYNTAX score. State-of the-art analytical methods are performed to calculate the serum levels of novel biomarkers: ceramides, acyl-carnitines, fatty acids, and proteins such as galectin-3, adiponectin, and the ratio of apolipoprotein B/apolipoprotein A1. Venous blood samples are collected before coronary angiography.
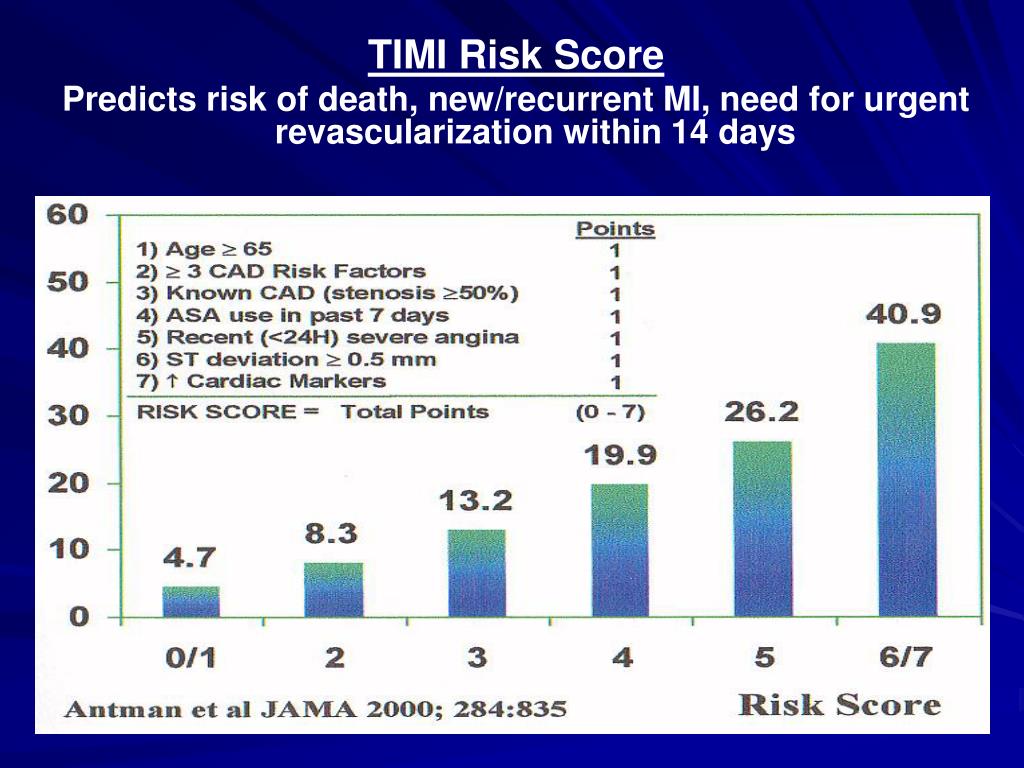
CAD RISK FACTORS TIMI TRIAL
Corlipid is a prospective, non-interventional cohort trial empowered to enroll 1065 patients with no previous coronary intervention history, who undergo coronary angiography in University Hospital AHEPA, Thessaloniki. This study aims to evaluate the diagnostic utility of plasma metabolomics-based biomarkers for determining the complexity and severity of CAD, as it is assessed via the SYNTAX score. Metabolomics is an emerging field in systems biology, which quantifies metabolic changes in response to disease progression. As oxygen and nutrient supply to the myocardium significantly decrease during ischemic periods, important changes occur regarding myocardial intermediary energy metabolism. Conversely, male sex, hypertension, and smoking did not independently correlate with fatal outcome.read more read lessĪbstract: Coronary artery disease (CAD) remains one of the leading causes of mortality and morbidity worldwide. This meta-analysis suggests that older age and diabetes are associated with higher risk of in-hospital mortality in patients infected by SARS-CoV-2.

A significant association between age and in-hospital mortality was confirmed in all multivariable models. At multivariable age-adjusted meta-regression analysis, diabetes was significantly associated with in-hospital mortality (coefficient: 1.02 95% CI 1.01–1.05 p = 0.043) conversely, hypertension was no longer significant after adjustment for age (coefficient: 1.00 95% CI 0.99–1.01 p = 0.820).
Male sex and smoking did not significantly affect mortality. The univariable meta-regression analysis showed a significant association between age (coefficient: 1.06 95% CI 1.04–1.09 p < 0.001), diabetes (coefficient: 1.04 95% CI 1.02–1.07 p < 0.001) and hypertension (coefficient: 1.01 95% CI 1.01–1.03 p = 0.013) with in-hospital death. The pooled estimate of in-hospital mortality was 12% (95% CI 9–15%). The analysis included 45 studies enrolling 18,300 patients. Univariable and multivariable age-adjusted analyses were conducted to evaluate the association between cardiovascular risk factors and the occurrence of in-hospital death. MEDLINE, Cochrane, Web of Sciences, and SCOPUS were searched for retrospective or prospective observational studies reporting data on cardiovascular risk factors and in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between cardiovascular risk factors and in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19. Abstract: A high prevalence of cardiovascular risk factors including age, male sex, hypertension, diabetes, and tobacco use, has been reported in patients with Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) who experienced adverse outcome.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
